Getting started
Quick introduction for developers
Getting started with our platform is easy. Follow these simple steps to download and connect our introductory demos to your application:
- Click Details button on your StarterApp-HS256 application to navigate to its details page.
- In the General section, under More Commands, click the Download config.js button and follow the provided instructions.
- Explore the cloned repository for examples and demos to help you get started.
Setting up an Identity Provider (IDP) for JWT-based authentication
The platform authenticate application clients, admins or operators using JWT-based tokens:
JSON Web Token (JWT) is a compact, URL-safe means of representing claims to be transferred between two parties. The claims in a JWT are encoded as a JSON object that is used as the payload of a JSON Web Signature (JWS) structure or as the plaintext of a JSON Web Encryption (JWE) structure, enabling the claims to be digitally signed or integrity protected with a Message Authentication Code (MAC) and/or encrypted.
See: JSON Web Token (JWT)
For applications authentication to work, it is necessary to set up an Identity Provider (IDP) which is responsible for authenticating users and providing them with valid JWT tokens.
Nowadays, most organizations use a third-party IDP as it simplifies the process and ensures that the authentication is secure and compliant with industry standards.
If you need additional guidance, we recommend you to explore the following solutions:
- Supabase - https://supabase.com/docs/guides/auth
- Auth0 - https://auth0.com
- Keycloak - https://www.keycloak.org
- Okta - https://www.okta.com
- Azure Active Directory - https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/active-directory
- AWS Cognito - https://aws.amazon.com/cognito
Also see: Integrating with IDPs and SSO providers using JSON Web Key Sets (JWKS)
Please note that if your organization's policies or compliance requirements do not allow re-using user's authentication tokens, you have the flexibility to implement an intermediate Security Token Service (STS) with the purpose of generating short-lived JWT authentication tokens for your users.
To authenticate WebSocket and HTTP clients, you need to set up authentication configuration in the authKey and adminKey properties.
Here's an example of an application that uses the RS256 JWT verification algorithm:
{
...
"appId": "b5cvf368e1fc006e95521000764a5706",
"name": "RS256 Example App",
"description": "This is an example application that uses RS256 JWT-based authentication",
"adminKey": {
"source": "raw",
"key": "-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----\nMIGbMBAGBy...RzY1gqGo=\n-----END PUBLIC KEY-----",
"algorithms": [
"RS256"
],
"issuer": []
},
"authKey": {
"source": "raw",
"key": "-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----\nMIGbMBAGBy...RzY1gqGo=\n-----END PUBLIC KEY-----",
"algorithms": [
"RS256"
],
"issuer": []
},
"adminSourceAddress": [
"0.0.0.0/0"
],
"clientSourceAddress": [
"0.0.0.0/0"
],
"enableWebSocketInboundTopic": true
}
Here is another using HS256 signatures:
...
"adminKey": {
"source": "raw",
"key": "cX1$wJT71Mölsd98.r97dC4DX",
"algorithms": [
"HS256"
],
"issuer": []
},
"authKey": {
"source": "raw",
"key": "xc5as087=)8a3p=?oidä+#ds$",
"algorithms": [
"HS256"
],
"audience": "www.example.org",
"issuer": []
}
...
The subscription and publication workflow
Applications provide a secure and isolated environment for authenticated clients to receive messages on topics of their choosing:
const ACCESS_TOKEN = "VALID JWT TOKEN HERE";
const ws = new WebSocket(
`wss://genesis.r7.21no.de/apps/${APP_ID}?access_token=${ACCESS_TOKEN}`
)
ws.onmessage = (event) => {
// Parse incoming WebSocket messages
const { topic, messageType, data } = JSON.parse(event.data);
if (topic === "main" && messageType === "welcome") {
// SESSION IS NOW READY, YOU CAN SUBSCRIBE TO APP TOPICS...
}
}
subscribe or unsubscribe to/from application topics:
...
ws.onmessage = (event) => {
const { topic, messageType, data } = JSON.parse(event.data)
if (topic === 'main' && messageType === 'welcome') {
ws.send(JSON.stringify({
type: 'subscribe',
data: {
topic: 'dashboard1'
}
}))
}
}
To publish a message into an application topic, a valid JWT token with the realtime:publisher:write:topic permission have to he provided in the Authorization header when calling the publish HTTP endpoint or via WebSocket client.
const APP_ID = 'YOUR APP ID HERE'
// verifiable via "app/configuration/authKey"
const ACCESS_TOKEN = 'VALID JWT TOKEN HERE'
const ws = new WebSocket(
`wss://genesis.r7.21no.de/apps/${APP_ID}?access_token=${ACCESS_TOKEN}`
)
ws.onmessage = async (event) => {
...
}
ws.send(JSON.stringify({
type: 'publish',
data: {
topic: 'main',
messageType: 'greeting',
compress: false,
payload: {
message: 'Greetings, fellow "sockets"!',
time: new Date().getTime()
}
}
}))
The
realtime:publisher:write:topic:mainpermission is required to be present in the JWT token to publish messages to themaintopic.
const APP_ID = 'YOUR_APP_ID'
// verifiable via "app/configuration/adminKey"
const AUTH_TOKEN = 'Bearer AUTH_TOKEN_HERE'
const reqHeaders = new Headers()
reqHeaders.append('Accept', 'application/json')
reqHeaders.append('Content-Type', 'application/json')
reqHeaders.append('Authorization', AUTH_TOKEN)
fetch(`https://genesis.r7.21no.de/api/topics/${APP_ID}/publish`, {
method: 'POST',
headers: reqHeaders,
body: JSON.stringify({
topic: 'main',
messageType: 'greeting',
message: {
msg: 'Hello subscribers in main topic 👋',
time: Date.now()
}
})
})
.then(() => console.log('Message published!')) // status code 201
.catch(console.error)
The
realtime:publisher:write:topic:mainpermission is required to be present in the JWT token to publish messages to themaintopic.
Example of a JWT token with the required permission (* means all topics):
{
"permissions": [
"realtime:publisher:write:topic:*"
],
"iss": "https://signer.example.com",
"sub": "service-name",
...
}
Publishing messages using the publish HTTP endpoint and Node.js
The following examples demonstrate how to publish messages using the publish HTTP endpoint with Node.js. Examples include the issuing of JWT authentication tokens with different signing algorithms:
const REQUIRED_PUBLISHER_PERMISSION = 'realtime:publisher:write:topic:*'
const axios = require('axios').default
const jwt = require('jsonwebtoken')
const fs = require('fs')
function publish (config, topic, message) {
console.info(`Publishing message into ${config.appId}/${topic} topic...`)
const AUTH_TOKEN = getAuthToken(config.adminSigningKey, 5)
const options = {
method: 'POST',
url: `https://${config.serverUrl}/api/topics/${config.appId}/publish`,
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json', Authorization: AUTH_TOKEN },
data: {
topic,
message,
compress: false
}
}
return axios.request(options)
}
function getAuthToken (secret, expiresIn) {
return 'Bearer ' + jwt.sign({ permissions: [REQUIRED_PUBLISHER_PERMISSION] }, secret, {
algorithm: 'RS256',
expiresIn,
issuer: 'https://signer.example.com',
subject: 'service-name'
})
}
publish(
{
serverUrl: 'genesis.r7.21no.de',
appId: '00000d863vb5baa987e8768ed3drrr09',
// private key of "adminKey.key" (public.pem)
adminSigningKey: fs.readFileSync('./private.pem')
},
'main', ,
'Hello World!'
)
.then(() => console.log('Message published!'))
.catch(err => console.error(err))
Creating RSA keys for JWT RS256 signing and verification using https://jwt-keys.21no.de:
const REQUIRED_PUBLISHER_PERMISSION = 'realtime:publisher:write:topic:*'
const axios = require('axios').default
const jwt = require('jsonwebtoken')
function publish (config, topic, message) {
console.info(`Publishing message into ${config.appId}/${topic} topic...`)
const AUTH_TOKEN = getAuthToken(config.adminSigningKey, 5)
const options = {
method: 'POST',
url: `https://${config.serverUrl}/api/topics/${config.appId}/publish`,
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json', Authorization: AUTH_TOKEN },
data: {
topic,
message,
compress: false
}
}
return axios.request(options)
}
function getAuthToken (secret, expiresIn) {
return 'Bearer ' + jwt.sign({ permissions: [REQUIRED_PUBLISHER_PERMISSION] }, secret, {
algorithm: 'HS256',
expiresIn,
issuer: 'https://signer.example.com',
subject: 'service-name'
})
}
publish(
{
serverUrl: 'genesis.r7.21no.de',
appId: '00000d863vb5baa987e8768ed3drrr09',
// value from "adminKey.key"
adminSigningKey: '**********'
},
'main',
'Hello World!'
)
.then(() => console.log('Message published!'))
.catch(err => console.error(err))
Creating secret key for JWT HS256 signing and verification using https://jwt-keys.21no.de:
const REQUIRED_PUBLISHER_PERMISSION = 'realtime:publisher:write:topic:*'
const axios = require('axios').default
const jwt = require('jsonwebtoken')
const fs = require('fs')
function publish (config, topic, message) {
console.info(`Publishing message into ${config.appId}/${topic} topic...`)
const AUTH_TOKEN = getAuthToken(config.adminSigningKey, 5)
const options = {
method: 'POST',
url: `https://${config.serverUrl}/api/topics/${config.appId}/publish`,
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json', Authorization: AUTH_TOKEN },
data: {
topic,
message,
compress: false
}
}
return axios.request(options)
}
function getAuthToken (secret, expiresIn) {
return 'Bearer ' + jwt.sign({ permissions: [REQUIRED_PUBLISHER_PERMISSION] }, secret, {
algorithm: 'ES512',
expiresIn,
issuer: 'https://signer.example.com',
subject: 'service-name'
})
}
publish(
{
serverUrl: 'genesis.r7.21no.de',
appId: '00000d863vb5baa987e8768ed3drrr09',
// private key of "adminKey.key"
adminSigningKey: fs.readFileSync('./private.pem')
},
'main',
'Hello World!'
)
.then(() => console.log('Message published!'))
.catch(err => console.error(err))
Creating ECDSA keys for JWT ES512 signing and verification https://jwt-keys.21no.de:
Restricting access to your application endpoints
To enhance security, administrators can restrict application access by defining allowed CIDR masks or IP addresses for both administrators and clients. This added layer of protection ensures that only authorized networks are permitted, further safeguarding sensitive data and communications.
- HTTP requests to server admin endpoints from IP addresses outside the ranges defined in
adminSourceAddressare rejected with 401 HTTP Status Code - Client connections from IP addresses outside the ranges defined in
clientSourceAddressare rejected and the WebSocket connection is immediately terminated
Configuration example:
...
"adminSourceAddress": [
"10.1.0.0/16",
"172.15.0.5",
"172.15.0.10"
"!172.15.6.66"
],
"clientSourceAddress": [
"10.2.0.0/16",
"!172.15.6.66"
]
...
Up to 10 CIDR ranges or IP addresses can be defined on each property
By default, the following ALLOW FROM ANYWHERE configuration is applied:
Please note that configurations settings above are oriented to restrict access to the realtime applications and not to Admin Console or Management APIs
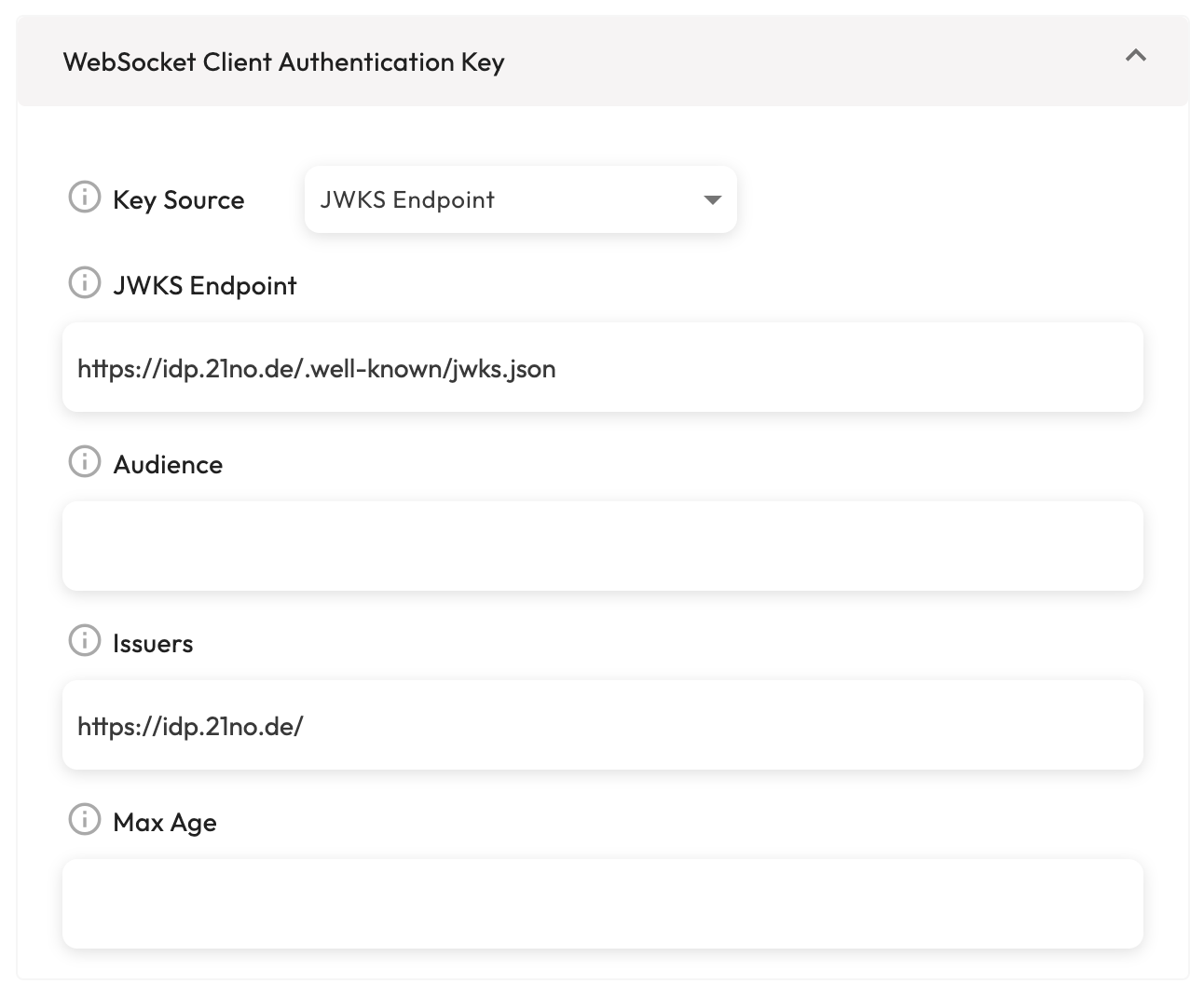
Generating WebSocket auth tokens using 21no.de Identity Provider
The 21no.de Identity Provider solution is is an evolving service that provides a secure and easy way to authenticate users and devices and generate JWT tokens.
Currently, the service allows the generation of JWT tokens for anonymous users and devices. In the context of Realtime Pub-Sub, applications in development phase, or when in need for supporting un-authenticated (anonymous) WebSocket connections can generate JWT tokens as follows:
const ACCESS_TOKEN = await fetch("https://idp.21no.de/token/anonymous", {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
},
body: JSON.stringify({
alg: "ES512", // https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Elliptic-curve_cryptography
}),
})
.then((res) => res.json())
.then((data) => data.access_token);
Your realtime application should be configured as follows: